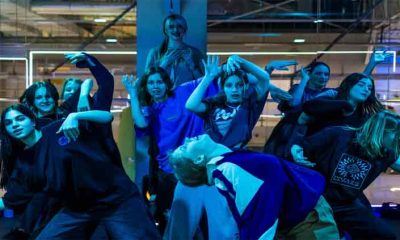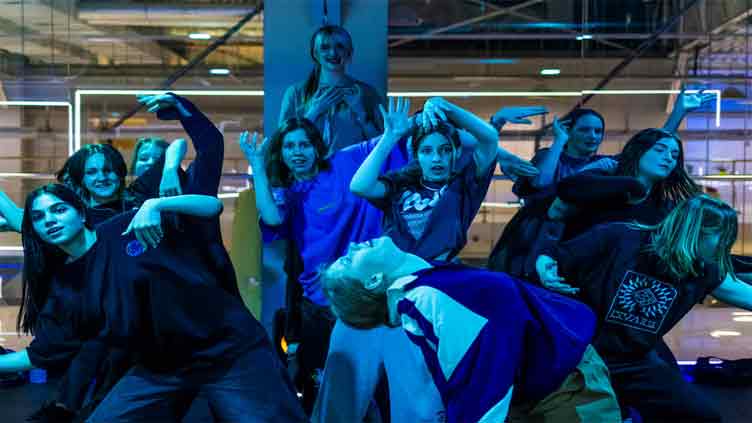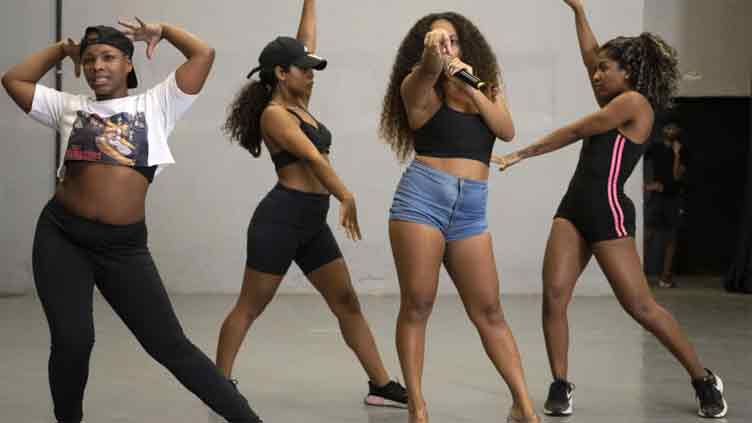Born in impoverished favelas, Rio de Janeiro funk music has emerged as a global phenomenon, embraced by superstars from Anitta to Beyonce and starring in museum shows – though it still faces stigma in Brazil.
Blending hip-hop and electronic music with Afro-Brazilian beats, funk emerged in the late 1990s in Rio, fuelling massive, all-night parties in the favelas, or slums, before spreading to other Brazilian cities and beyond.
Now, funk is having a moment.
Beyonce sampled Brazilian funk legend O Mandrake for “Spaghettii”, a track on “Cowboy Carter,” the hit album she released last month.
Anitta, the Rio-born sensation who has done more than anyone to take the genre global, has her own new album coming out Friday, “Funk Generation.”
Fellow funk star Ludmilla performed this month at Coachella, the high-profile music festival in California.
With museum expos and even an artist-in-residence program dedicated to the genre, funk is suddenly everywhere.
“Funk is a source of self-esteem for the favelas,” says writer Taisa Machado, founder of online platform Afrofunk Rio.
“Those of us who work with funk always knew its power, its musical and cultural quality. We’ve been waiting for this moment,” she tells AFP.
FROM STREET TO MUSEUM
In Lapa, a trendy nightspot in central Rio, a dozen youths from the favelas and city outskirts are rehearsing their final show for #estudeofunk, a residency programme at the Fundicao Progresso cultural centre.
Four girls in tight-fitting athletic gear and streetwear are practicing their dance moves under the watchful eye of their director.
The goal is to “professionalize” their knowledge and turn their passion into a marketable skill, says the woman behind the project, Vanessa Damasco.
“I want to be able to make a living from my music, my art,” says funk singer Gustavo de Franca Duarte after rehearsal.
The 35-year-old father of four is a night watchman. But Duarte’s dream is to make it as “MC Gut Original” – his stage name.
Things have also gotten funky at the Rio Museum of Art, which is currently hosting an exhibit with hundreds of photographs, paintings, videos and installations devoted to the music and the iconic dance parties it fuels, known as “baile funk”.
The show, which has drawn large crowds, also highlights key moments in the genre’s mainstream arrival, like when Olympic medallist Rebeca Andrade, Brazil’s most famous gymnast, used it in the soundtrack for her floor routine at the Tokyo Games in 2021.
One of the artists on display is French photographer Vincent Rosenblatt, who has been documenting “baile funk” for 15 years in a sensual body of work that was also exhibited in Paris recently.
He started shooting funk parties around the time Rio officially declared funk part of the city’s cultural heritage, in 2009.
But the music “had to fight” to get there, he says: the same day the city council adopted the designation, it also revoked a law restricting funk parties.
LIKE A ‘PHOENIX’
Funk music is about “day-to-day life in a favela, teen trends, slang,” says anthropologist and filmmaker Emilio Domingos, the screenwriter for a 2020 Netflix documentary about Anitta.
“The lyrics talk about the favela as a place of pride.”
But the songs are also tinged with references to the drug trafficking and violence that permeate the favelas.
That has fed the stigma the genre faces.
Ironically, just as funk is booming on the world stage, “baile funk” parties are growing less common in Brazil.
“Funk moves a lot of money, it creates jobs, it opens up important debates and has the power to exert a positive influence,” says Machado, the writer.
But “it also faces a lot of prejudice, racism, machismo and elitism.”
Rosenblatt, the photographer, agrees.
But “funk is like the phoenix: the more they try to repress it, the more it will be reborn somewhere else,” he says.
Related Topics
Post Views: 12


 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months ago
 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months ago
 Fashion2 months ago
Fashion2 months ago
 pakistan3 months ago
pakistan3 months ago
 pakistan3 months ago
pakistan3 months ago
 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months ago
 World2 months ago
World2 months ago
 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months ago